Answer: Resulting solution will not be neutral because the moles of
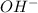 ions is greater. The remaining concentration of
ions is greater. The remaining concentration of
![[OH^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/dr3vksfxq7ot5rvw2mjmnw96oc1xtussa2.png) ions =0.0058 M.
ions =0.0058 M.
Explanation:
Given,
[HCl]=0.100 M
![[HNO_3]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/czjwp9qnhoks9dk84kx2cacbxusfu6n5jt.png) = 0.200 M
= 0.200 M
![[Ca(OH)_2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/q37y8kfd3dvoe190ygj8v2w2wzd14h9532.png) =0.0100 M
=0.0100 M
[RbOH] =0.100 M
Few steps are involved:
Step 1: Calculating the total moles of
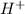 ion from both the acids
ion from both the acids
moles of
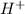 in HCl
in HCl
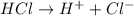
if 1 L of
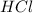 solution =0.100 moles of HCl
solution =0.100 moles of HCl
then 0.05L of HCl solution= 0.05
 0.1 moles= 0.005 moles (1L=1000mL)
0.1 moles= 0.005 moles (1L=1000mL)
moles of
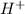 in HCl = 0.005 moles
in HCl = 0.005 moles
Similarliy
moles of
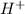 in
in
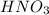
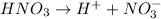
If 1L of
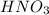 solution= 0.200 moles
solution= 0.200 moles
Then 0.1L of
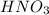 solution= 0.1
solution= 0.1
 0.200 moles= 0.02 moles
0.200 moles= 0.02 moles
moles of
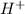 in
in
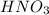 =0.02 moles
=0.02 moles
so, Total moles of
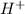 ions = 0.005+0.02= 0.025 moles .....(1)
ions = 0.005+0.02= 0.025 moles .....(1)
Step 2: Calculating the total moles of
![[OH^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/dr3vksfxq7ot5rvw2mjmnw96oc1xtussa2.png) ion from both the bases
ion from both the bases
Moles of
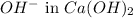
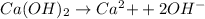
1 L of
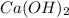 = 0.0100 moles
= 0.0100 moles
Then in 0.5 L
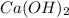 solution = 0.5
solution = 0.5
 0.0100 moles = 0.005 moles
0.0100 moles = 0.005 moles
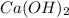 produces two moles of
produces two moles of
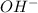 ions
ions
moles of
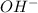 = 0.005
= 0.005
 2= 0.01 moles
2= 0.01 moles
Moles of
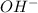 in
in
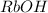
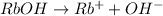
1 L of RbOH= 0.100 moles
then 0.2 [RbOH] solution= 0.2
 0.100 moles = 0.02 moles
0.100 moles = 0.02 moles
Moles of
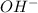 = 0.02 moles
= 0.02 moles
so,Total moles of
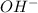 ions = 0.01 + 0.02=0.030 moles ....(2)
ions = 0.01 + 0.02=0.030 moles ....(2)
Step 3: Comparing the moles of both
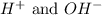 ions
ions
One mole of
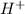 ions will combine with one mole of
ions will combine with one mole of
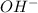 ions, so
ions, so
Total moles of
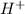 ions = 0.005+0.02= 0.025 moles....(1)
ions = 0.005+0.02= 0.025 moles....(1)
Total moles of
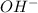 ions = 0.01 + 0.02=0.030 moles.....(2)
ions = 0.01 + 0.02=0.030 moles.....(2)
For a solution to be neutral, we have
Total moles of
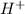 ions = total moles of
ions = total moles of
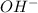 ions
ions
0.025 moles
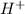 will neutralize the 0.025 moles of
will neutralize the 0.025 moles of
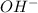
Moles of
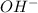 ions is in excess (from 1 and 2)
ions is in excess (from 1 and 2)
The remaining moles of
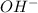 will be = 0.030 - 0.025 = 0.005 moles
will be = 0.030 - 0.025 = 0.005 moles
So,The resulting solution will not be neutral.
Remaining Concentration of
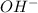 ions =
ions =
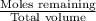
![[OH^-]=(0.005)/(0.85)=0.0058M](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/bqlnlb3s1g81arbm7bp98uz729vjra1c2t.png)