Answer:- The lung contains 0.12 moles of air when it's full.
Solution:- At constant temperature and pressure, the volume is directly proportional to the moles of the gas.
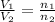
where,
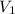 and
and
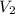 are the initial and final volumes. Similarly,
are the initial and final volumes. Similarly,
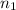 and
and
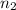 are the initial and final moles of the air.
are the initial and final moles of the air.
Let's plug in the given values in the formula and solve this for initial moles of the gas.
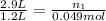
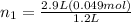
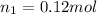
So, the lung contains 0.12 moles of air when it's full.