Answer:
If the gas is ideal while volume and temperature stay unchanged, there would be a five-fold increase in the pressure of this gas.
Step-by-step explanation:
Let
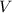 denote the volume of this gas, let
denote the volume of this gas, let
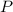 denote the pressure of the gas, let
denote the pressure of the gas, let
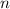 denote the number of particles in this gas, let
denote the number of particles in this gas, let
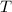 denote the temperature of this gas, and let
denote the temperature of this gas, and let
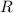 denote the ideal gas constant.
denote the ideal gas constant.
If this gas is an ideal gas, it would satisfy the ideal gas law:
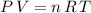 .
.
Assuming that this gas is uniform. The mass of this gas will be directly proportional to the number of particles
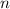 in this gas. Hence, a five-fold increase in the mass of this will increase the number of particles in this gas by five folds.
in this gas. Hence, a five-fold increase in the mass of this will increase the number of particles in this gas by five folds.
Rearrange this equation to separate pressure
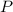 from the number of particles in this gas
from the number of particles in this gas
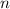 :
:
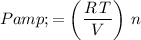 .
.
In other words, if the temperature and volume of this gas stays the same, the pressure
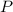 of this gas will be proportional to the number of particles
of this gas will be proportional to the number of particles
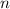 in this gas. Thus, the five-fold increase in the number of particles (from a five-fold increase in mass) will increase the pressure of this gas by five folds.
in this gas. Thus, the five-fold increase in the number of particles (from a five-fold increase in mass) will increase the pressure of this gas by five folds.