Here we have to get the moles of oxygen present in the human lungs at the given condition.
The moles of oxygen present in the lungs are 0.025.
The moles of oxygen present in the lung at 21.1 kilo-pascals partial pressure and 295 K temperature with keeping the maximum intake of oxygen, as given i.e. 3.0 L can be obtained from the ideal gas equation.
The ideal gas equation is PV=nRT (where, P = Pressure, or, 21.1 kilo-pascal; V = volume or, 3.0 L; n = number of moles of oxygen present in the lungs; R = molar gas constant, or, 8.314 L.kPa.K⁻¹.mole⁻¹ and T = temperature or, 295 K.
Now the ideal gas equation can be rewritten as-
n=
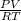 . On plugging the given values, we get,
. On plugging the given values, we get,
n =
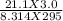
Or, n = 0.025 mole
Thus the moles of oxygen present in lungs are 0.025 mole.