Option D: 15.4
There are following rules for manipulating equilibrium constant:
1. On adding two equilibrium reactions, their equilibrium constant gets multiplied.
For example:
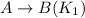
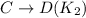
On adding two reactions,
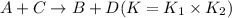
2. On subtracting two equilibrium reactions, their equilibrium constant gets divided.
For example:
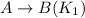
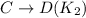
On subtracting two reactions,
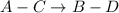
Or,
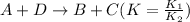
3. If an equilibrium reaction is multiplied by any constant, it goes to the power of its equilibrium constant.
For example:
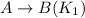
Thus,
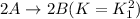
4. On reversing an equilibrium reaction, the equilibrium constant of reversed reaction becomes inverse of the original value.
For example:
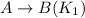
Thus,
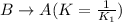
Now, the given equilibrium reaction is as follows:
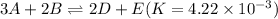
To get the desired reaction, first reverse the above reaction as follows:
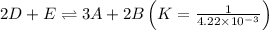
Now, multiply the above reaction with 1/2,
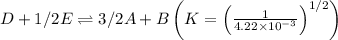
Thus,
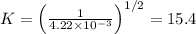
Therefore, equilibrium constant for the resultant reaction is 15.4 that is option D.