Answer:
The 64 weeks
Step-by-step explanation:
Thinking process:
First we gather the data:
1700lbm = 771.107 kg
225 milliNewtons = 0.225 N
Final velocity = 420 mil/min = 11 265.4 m/s
Let the initial velocity, u₀ = 0 m/s
Final velocity = v m/s
Acceleration is given by the formula,
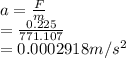
However, we know that the final velocity, v is given by
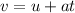
where u = 0
a = 0.0002918
t = ?
v = 11 265.4 m/s
substituting:
11 265.4 = 0 + (0.0002918) (t)
dividing both sides gives, t = 38 606 579 s
1 day = 86 400 s
t = 446.83 days
= 63.8 weeks
= 64 weeks