Dalton's atomic theory was based on the law of conservation of mass which states that the matter can neither be created nor be destroyed but it can only transformed into one form or another. In a chemical reaction, total mass of the reactants will be equal to the total mass of the products.
Taking an example,
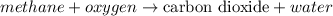
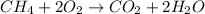
Mass of
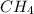 = 16g
= 16g
Mass of
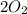 =
=
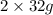
Total mass on reactant side =
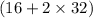
Total mass on reactant side = 80g
Mass of
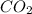 = 44g
= 44g
Mass of
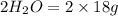
Total mass on product side =
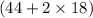
Total mass on product side = 80g
It is seen from the above example that the
total mass on reactant side = total mass on product side.