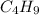Answer : The emperical formula of hydrocarbon is
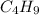 .
.
Solution : Given,
Mass of
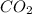 = 11.1 g
= 11.1 g
Mass of
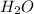 = 5.11 g
= 5.11 g
Step 1 : convert given mass in moles.
Moles of
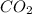 =
=
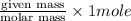 =
=
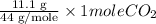 = 0.2522 moles
= 0.2522 moles
Moles of
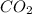 = moles of C = 0.2522 moles
= moles of C = 0.2522 moles
Moles of
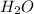 =
=
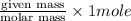 =
=
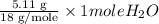 = 0.2838 moles
= 0.2838 moles
Moles of
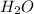 = moles of H = 0.2838 × 2 = 0.5677 moles
= moles of H = 0.2838 × 2 = 0.5677 moles
Step 2 : For the mole ratio, divide each value of moles by the smallest number of moles calculated.
For C = 0.2522/0.2522 = 1
For H = 0.5677/0.2522 = 2.25
C : H = 1 : 2.25
To make the ratio as a whole number multiply numerator and denominator by 4.
Ratio of C : H =
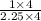 = 4 : 9
= 4 : 9
The mole ratio of the element is repersented by subscripts in emperical formula.
Therefore, the Emperical formula =