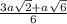The best way to do this is to draw a picture of ΔFKL and include line segment KM that is perpendicular to FL. This creates ΔFKM which is a 45°-45°-90° triangle and ΔLKM which is a 30°-60°-90° triangle.
Find the lengths of FM and ML. Then, FM + ML = FL
FM
ΔFKM (45°-45°-90°): FK is the hypotenuse so FM =
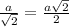
ML
ΔLKM (30°-60°-90°): from ΔFKM, we know that KM =
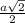 , so KL =
, so KL =
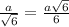
FM + ML = FL
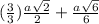
=