Answer :
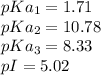
Explanation: Cysteine is a special amino acid having 3 protonable groups which means this group will have 3 pKa's.
The structures wit their pKa values are given in the image below.
pI or isoelectric point is the pH at which the amino acid have no net charge.
Therefore, in the case of cysteine the net charge is 0 in the structure B, so pI will be present between
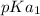 and
and
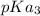 .
.
pKa values of cysteine are:
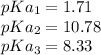
pI will be
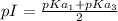
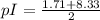
pI = 5.02