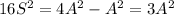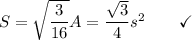An equilateral triangle isn't a right triangle, so the Pythagorean Theorem doesn't apply directly.
But if we divide an equilateral triangle with side s in half along an altitude, we get two congruent right triangles each with hypotenuse s and one leg s/2.
The other leg is the altitude h we divided along. By the Pythagorean Theorem
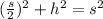
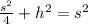
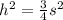
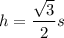
The area A of our original equilateral triangle is now
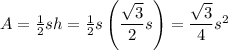
So the area of our equilateral triangle of side 5 is
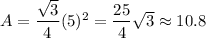
Answer: 10.8
I don't like ruining a nice exact answer with an approximation, but the question asks for one.
We could have done the above steps with 5 in particular instead of s but I prefer to do the general solution and substitute at the end.
----
Since you read this far, I will give you the secret formula for the area S of a triangle given squared sides A, B, C. Your teachers won't even know this one.
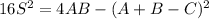
Let's try it out for
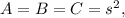 an equilateral triangle:
an equilateral triangle: