Answer: Option (2) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
Dynamic equilibrium is an equilibrium where rate of forward and reversible reactions are equal.
For example,
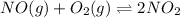
This reaction show rate at which reactants are combining is equal to the rate of formation of nitrogen dioxide.
Also, here the concentration of reactants is equal to the concentration of products.
Thus, we can conclude that out of the given options the reaction does not go to completion does not describe the given reaction.