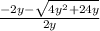We know that g(x) = \frac{3}{x^2+2x}
We have to find g^-1(x) or inverse of g(x)
Inverse of g(x) can be determined by equating g(x) to y, and determining the value of x in terms of y
g(x) = y = \frac{3}{x^2+2x}
⇒ y × (x² + 2x) = 3
⇒ yx² + 2xy = 3
⇒ yx² + 2yx - 3 = 0
Determining the roots of x using:
x =
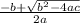 OR x =
OR x =
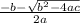 , where a is coefficient of x², b is coefficient of x, and c is the constant
, where a is coefficient of x², b is coefficient of x, and c is the constant
⇒ x =
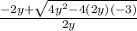 OR x =
OR x =
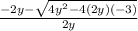
⇒ x =
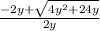 OR x =
OR x =
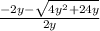
Hence, g^-1(x) =
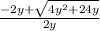 OR x =
OR x =