The equilibrium reaction is as follows:
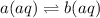
The initial number of moles of a (aq) and volume of solution is given 0.134 mol and 250 mL.
First calculate the molarity of solution which is defined as number of moles of solute in 1 L of solution.
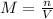
Putting the values,
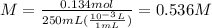
Thus, initial concentration of a(aq) will be 0.536 M.
At equilibrium, let the change in concentration be x, thus, concentration of a(aq) will be 0.536-x and that of b(aq) will be x.
The expression for
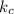 for the equilibrium reaction is:
for the equilibrium reaction is:
![k_(c)=([b])/([a])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/ql5p755du049a9cjkorlfe5gl9xpfong1l.png)
Here [a] and [b] are equilibrium concentration of reactant a and product b respectively.
Putting the values,
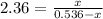
On rearranging,
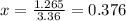
Now, equilibrium concentration of a (aq) will be:
![[a]=0.536-x=0.536-0.376=0.16 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/5btnhiyafqa73a20h081ev998snkhptf0n.png)
Therefore, equilibrium concentration of a(aq) is 0.16 M