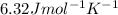The mathematical expression for heat capacity at constant pressure is given as:
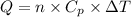 (1)
(1)
where, Q = heat capacity
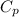 = molar heat capacity at constant pressure
= molar heat capacity at constant pressure
 = change in temperature
= change in temperature
n = number of moles
Therefore,
 =
=
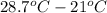
=
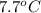
Number of moles =
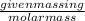
=
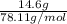
= 0.186 mole
Put the values in formula (1)
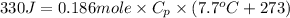 (conversion of degree Celsius into kelvin)
(conversion of degree Celsius into kelvin)
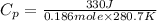
=
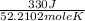
= 6.32 J /mol K
Hence, molar heat capacity of benzene at constant pressure =