The acceleration of the car,
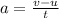
Here, v is final velocity, u is initial velocity and t is time taken by the car.
Given
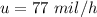 ,
,
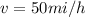 and
and
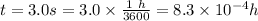
Therefore, from above equation
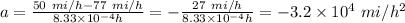 .
.
Here, negative sign shows deceleration of a car.
Thus the the magnitude of car acceleration is
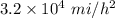 .
.