Answer:
(a) 2.002 bar
(b) 1284 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
pv¹°³⁵ = constant
p v¹°³⁵ = k ------------------(a)
This implies that
p₁v₁¹°³⁵ = p₂v₂¹°³⁵ -----------------(i)
Where;
p₁ and v₁ are the state 1 pressure and volume of the gas respectively.
p₂ and v₂ are the state 2 pressure and volume of the gas respectively.
(a) From the question;
p₁ = 20bar
v₁ = 0.5m³
p₂ = unknown
v₂ = 2.75m³
Substitute these values into equation (i) as follows;
=> 20 x 0.5¹°³⁵ = p₂ x 2.75¹°³⁵
=> 20 x 0.3923 = p₂ x 3.9183
=> 7.846 = p₂ x 3.9183
Solve for p₂ ;
p₂ = 7.846 / 3.9183
p₂ = 2.002 bar
Therefore, the pressure at state 2, in bar, is 2.002
(b) The work done, W, is given by
W =
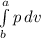 ----------------(ii)
----------------(ii)
Where;
a and b are the states 2 and 1 values of the volume of the gas. i.e
a = v₂ = 2.75m³
b = v₁ = 0.5m³
Calculate the value of k in equation (a) as follows;
p₁v₁¹°³⁵ = k
k = 20 x 0.5¹°³⁵
k = 7.846
From equation (a), we can then write;
=> p = 7.846 v⁻¹°³⁵
W =
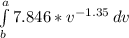
W = 7.846 x
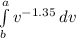
Substitute the limits a and b;
W = 7.846 x [
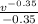 ]
]
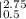
W = 7.846 [
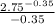 -
-
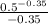 ]
]
W = 7.846 [-2.005 - (-3.6416)]
W = 7.846 [-2.005 + 3.6416]
W = 7.846 [1.6366]
W = 12.84 bar.m³
1 bar = 10⁵N/m²
12.84 bar = 12.84 x 10⁵N/m²
=> 12.84 bar.m³ = 12.84 x 10⁵ Nm = 1284000Nm = 1284000J = 1284 kJ
Therefore, the workdone is 1284 kJ