We use the kinematic equation,
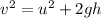
Here, u is initial velocity, and v is final velocity, g is acceleration due to gravity and h is maximum height.
The velocity of the astronaut reaching the ground from h is
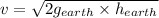
Here, u = 0.
Similarly, for moon
 .
.
Take,
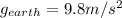 and
and
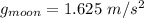 .
.
For safe jump to the ground, the velocity should be same.
Therefore,
![\sqrt{2 g_(earth) * h_(earth) } = \sqrt{2 g_(moon) * h_(moon) } \\\\ </p><p>[tex]9.8 m/s^2 * 1.2 \ m = 1.625 m/s^2 * h_(moon) \\\\ h_(moon) = (11.76)/(1.625) = 7.2 \ m](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/physics/college/vm3stfn3ofan32rylmnhz5npgv4h190sh0.png)
Thus, the astronaut safely jump to the ground on the moon from height 7.2 m.