Glucose freezes at -3.75 °C and freezing point of pure water is 0 °C. Thus, depression in freezing point or
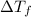 can be calculated as follows:
can be calculated as follows:
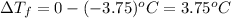
It is related to molal concentration as follows:
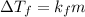
Here,
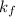 is freezing point depression constant.
is freezing point depression constant.
Rearranging to calculate molal concentration:
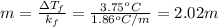
Therefore, molal concentration of glucose in the solution will be 2.02 m.