Consider right triangle ΔABC with legs AC and BC and hypotenuse AB. Draw the altitude CD.
1. Theorem: The length of each leg of a right triangle is the geometric mean of the length of the hypotenuse and the length of the segment of the hypotenuse adjacent to that leg.
According to this theorem,
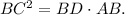
Let BC=x cm, then AD=BC=x cm and BD=AB-AD=3-x cm. Then
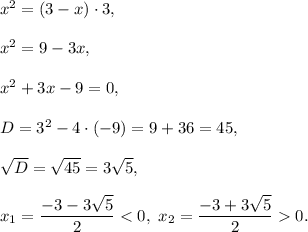
Take positive value x. You get
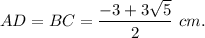
2. According to the previous theorem,
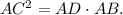
Then
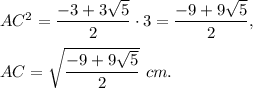
Answer:
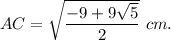
This solution doesn't need CD=2 cm. Note that if AB=3cm and CD=2cm, then
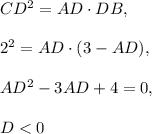
This means that you cannot find solutions of this equation. Then CD≠2 cm.