The balanced chemical reaction will be as follows:
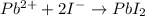
To determine the % yield, first calculate the theoretical yield.
Molairty and volume of
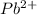 is 0.218 M and 65 mL respectively. Convert it into number of moles as follows:
is 0.218 M and 65 mL respectively. Convert it into number of moles as follows:
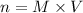
Here, volume should be in L thus,
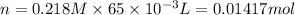
Similarly, calculate number of moles of iodide ion,
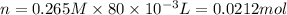
Now, from the balanced chemical equation, 1 mole of
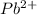 gives 1 mol of
gives 1 mol of
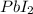 , thus, 0.01417 mol will give 0.01417 mol of
, thus, 0.01417 mol will give 0.01417 mol of
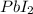 .
.
Also, 2 mole of
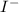 will give 1 mole of
will give 1 mole of
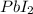 thus, 0.0212 mol will give,
thus, 0.0212 mol will give,

Molar mass of
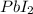 is 461.01 g/mol calculating mass of
is 461.01 g/mol calculating mass of
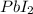 obtained from
obtained from
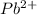 and
and
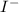 as follows:
as follows:
From
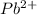 :
:
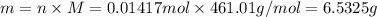
Similarly, for
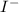 :
:
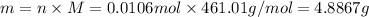
Here,
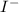 is limiting reactant as it produced less amount of
is limiting reactant as it produced less amount of
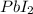 as compared with
as compared with
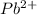 .
.
Theoretical yield is amount of product obtained from limiting reactant thus, theoretical yield will be 4.8867 g.
Percentage yield can be calculated as follows:
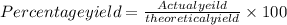
Actual yield is 3.26 g thus, percentage yield will be:
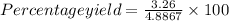 =66.7%
=66.7%
Therefore, % yield will be 66.7%