For the first derivative of f(x), we will use the product rule and the power rule.
The power rule states,
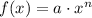
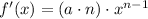
The product rule states,
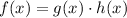
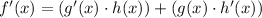
When a constant without any variable is derived, it becomes equal to 0, so any constants that are derived can be eliminated.
With these rules in mind, derive the function f(x).
First, we will set the terms in parentheses to equal separate functions for convenience:
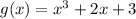
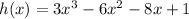
Derive these separate functions for f'(x):
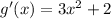
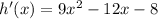
Apply the product rule for f(x):
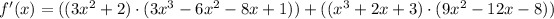
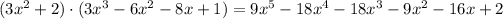
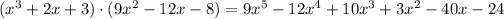
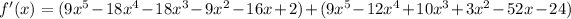
Combining like terms, we get the following result:
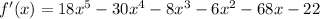
Derive this function once again to get f''(x):
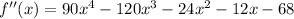
The question asks for the coefficient of the squared term. Look at f''(x), then look for the term with the degree of 2:
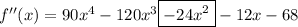
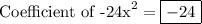
The coefficient of the squared term of f''(x) will be -24.