Answer : The approximate relation Celsius = 1/2 Fahrenheit is a better approximation at higher temperatures
Explanation :
The formula for Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion is
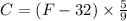
At lower temperature the value that needs to be subtracted (32) is large enough as a result the approximation "celsius = 1/2 fahrenheit " does not seem valid.
For example, 50 F is 10°C.
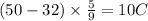
This is almost 1/5 of Fahrenheit temperature.
But at higher temperatures , the value becomes insignificant and also the ratio 5/9 tend to be equal to 0.5.
For example, 2000 F is 1093°C
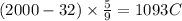
This is almost half of Fahrenheit temperature.
Therefore , the approximate relation Celsius = 1/2 Fahrenheit is a better approximation at higher temperatures