Answer:
The ratio of the concentration of a conjugate base over weak acid describes the proportions of a weak acid necessary to satisfy the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
Step-by-step explanation:
The Henderson Hesselbach equation is given as:
![pH=pK_a+\log ([Salt])/([Acid])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/craozjfpa3obt0t77p1itedc8fkszbu76b.png)
pH = potential of H
![pK_a=-\log [K_a]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/kcqop1rlxvmkq89f63wu7yog5wbyerhecx.png)
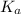 =Dissociation constant
=Dissociation constant
[Salt] = Concentration of salt
[Acid] = Concentration of acid
Or it can also be represented as:
WeaK acid
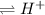 + Conjugate base
+ Conjugate base
![pH=pK_a+\log \frac{[\text{conjugate base}]}{[\text{weak acid}]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/7agdzpuid02hexo783f2uqr2z03w5i7gx9.png)
[conjugate base] = Concentration of conjugate base formed from the dissociation of weak acid.
[weak acid] = Concentration of weak acid.