Answer : The heat required will be, 20.35 KJ
Explanation : Given,
Molar mass of
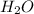 = 18 g/mole
= 18 g/mole
First we have to calculate the moles of
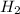
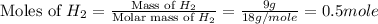
Now we have to calculate the heat produced.
Formula used :
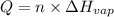
where,
Q = heat required = ?
n = moles of water = 0.5 mole
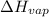 = 40.7 KJ/mole
= 40.7 KJ/mole
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get the heat required.
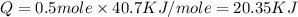
Therefore, the heat required will be, 20.35 KJ