5 a)
Start by arranging the materials by the sonic speed and then their physical state:
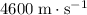 - Copper (solid)
- Copper (solid)
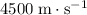 - Glass (solid)
- Glass (solid)
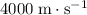 - Wood (solid)
- Wood (solid)
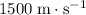 - Sea Water (liquid)
- Sea Water (liquid)
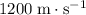 - Acetone (liquid)
- Acetone (liquid)
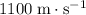 - Alcohol (liquid)
- Alcohol (liquid)
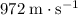 - Helium (gas)
- Helium (gas)
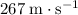 - Carbon dioxide (gas)
- Carbon dioxide (gas)
What trend do you identify from these data? Here's what I've got:
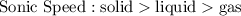
5 b)
The way microscopic particles are arranged in a substance helps distinguish between different physical states:
- Particles in a solid are held tightly in place with small separation in between; it's hard for particles in a solid to move past one another; solids therefore have shapes that persists over time.
- Particles in a gas are highly mobile- they keep moving AT ALL TIMES. There are large separations between individual particles and therefore gases tend to show no definite shape or volume.
- The arrangement of particles in a liquid is located somewhere in between that of solids and gases. The exact configuration is dependent on the nature of the liquid- for example, molecules in maple syrup are held way closer to each other than those in distilled water are.
Sound travels as a longitudinal wave. As a sound wave passes through a medium, individual particles become excited and gain energy; as they run into others they transfer their energy to the next particle; the sound wave thus propagate across the medium. With a lower average distance between individual particles this action can proceed at a greater rate in average solids than in average liquids, and in average liquids than in average gases. Hence the trend.