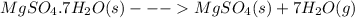All hydrates have some amount of water of hydration present associated with their crystal structure. When such hydrated compounds are heated, the water of hydration is driven off from the molecular arrangement. For example, epsom salt is heptahydrate of magnesium sulfate. So, when epsom salt is heated it loses the water of hydration to form anhydrous magnesium sulfate. So anhydrous magnesium sulfate would remain after heating epsom salt to remove the water of hydration.