Rotational symmetry is defined as the property a shape has when it looks the same after some rotation by partial turns.
Also, for a figure to have rotational symmetry the shape must look exactly the same during rotation, at least once, before it is rotated by
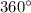 .
.
In the figures given above, when figure 'B' is rotated by
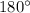 , we get the same image as the previous. So, figure 'B' has rotational symmetry.
, we get the same image as the previous. So, figure 'B' has rotational symmetry.
Similarly, in the figure 'D' it can be observed that when it is rotated by
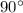 , we get the same image. Therefore, figure 'D' too has a rotational symmetry.
, we get the same image. Therefore, figure 'D' too has a rotational symmetry.
Whereas, the figures 'A' and 'C' do not show any rotational symmetry. Therefore, only figure 'B' and 'D' have the rotational symmetry.