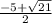Answer:
Option B is correct.
u= x+4
Explanation:
Solve the equation:
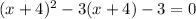
Using substitution:
Let u = x+4
then;
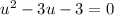 ....[1]
....[1]
For a quadratic equation
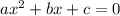 ....[2], then the solution is given by:
....[2], then the solution is given by:
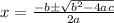
On comparing equation [1] and [2] we have;
a = 1 , b = -3 and c = -3
then;
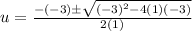
⇒
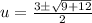
⇒
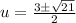
Substitute u = x+4
then;
⇒
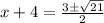
Subtract 4 from both sides we have;
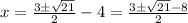
⇒
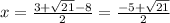
and
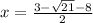
⇒
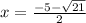
Therefore, the solution for the given equation are,
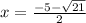 ,
,