The formula for depression of freezing point is:
 -(1)
-(1)
where,
 is depression of freezing point,
is depression of freezing point,
 is freezing point depression constant and
is freezing point depression constant and
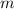 is molality.
is molality.
Freezing point of pure water =
 (given)
(given)
Freezing point of glucose =
 (given)
(given)
Depression of freezing point,
 =
=

Substituting the values:

Substituting the values in formula (1):


Hence, the the molal concentration of glucose in the given solution is
 .
.