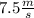Answer:
It is
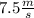 in the same direction of the shell's velocity but in the opposite sense.
in the same direction of the shell's velocity but in the opposite sense.
Step-by-step explanation:
In order to calculate the velocity of the cannon, we are going to use the Momentum Conservation Law.
If the exterior resultant force acting over a particles system is nule therefore the momentum is constant.
We can calculate the momentum as
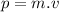
Where ''p'' is the momentum (a vectorial magnitude)
Where ''m'' is the mass of the object
And where ''v'' is the velocity (a vectorial magnitude)
In the exercise, the momentum is constant (because the exterior resultant force is equal to zero).
So we can write :
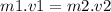 (I)
(I)
Where m1 is the mass of the shell
Where v1 is the velocity of the shell
Where m2 is the mass of the cannon
And where v2 is the velocity of the cannon.
Replacing all the data in the equation (I) :
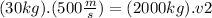
If we solve to find v2 :
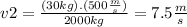
We find that the resulting velocity of the cannon is