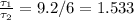during the acceleration the time taken to reach full speed is 6 s
so angular acceleration will be given as
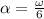
now from the same maximum speed it will stop in time t = 9.2 s
so deceleration is given as
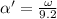
now we can say initially the torque will be given as
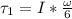
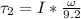
now we have