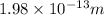Answer: 1.98\times10^{-13}m[/tex]
We need to find the wavelength of the deutrons which are travelling with a velocity of
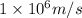 . we would use de-Broglie's formula which relates momentum of the particle with its wavelength.
. we would use de-Broglie's formula which relates momentum of the particle with its wavelength.
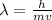
where, h = Planck's constant
m is the mass
v is the velocity
and
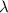 is the wavelength.
is the wavelength.
Deutron has 1 neutron and 1 proton.
Mass of deutron is
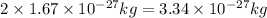 (because of mass of proton =mass of neutron =
(because of mass of proton =mass of neutron =
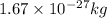
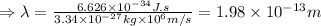
Therefore, the wavelength of the deutrons travelling with the speed
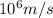 is
is