Answer:
A reaction between a strong acid and a weak base.
Step-by-step explanation:
The conjugate acid of a weak base is a strong acid.
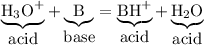
The reaction above is reversible, so we can write
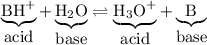
Thus, the solution of the salt will be acidic, because it produces hydronium ions.
Example;
Ammonium chloride is the salt of a strong acid (HCl) and a weak base (NH₃).
Solutions of NH₄Cl are acidic.