Answer :
The correct answer for Mass of Na₂HPO₄ = 4.457 g and mass of NaH₂PO₄ = 8.23 g
Given : pH = 6.86
Total concentration of Phosphate buffer = 0.1 M
Asked : Mass of Sodium phosphate monobasic (NaH₂PO₄) = ?
Mass of Sodium phosphate dibasic(Na₂HPO₄)= ?
Following steps can be done to find the masses of NaH₂PO₄ and Na₂HPO₄ :
(In phosphate buffer , Na+ ion from NaH₂PO₄ and Na₂HPO₄ acts as spectator ion , so only H₂PO₄⁻ and HPO₄²⁻ will be considered )
Step 1 : To find pka
H₂PO₄⁻ <=> HPO₄²⁻
The above reaction has pka = 7.2 ( from image shown )
Step 2 : Plug values in Hasselbalch- Henderson equation .
Hasselbalch -Henderson equation is to find pH for buffer solution which is as follows :
![pH = pka + log([A^-])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/vn1a5fme55wae9mtulevcvqp4enc2m77rs.png)
pH = 6.86 pKa = 7.2
![6.86 = 7.2 + log ([HPO_4^2^-])/([H_2PO_4^-])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/a4mo87ujje6rmgnidtiefsmg5zwjp79se0.png)
Subtracting both side by 7.2
![6.86-7.2 = 7.2 -7.2+ log ([HPO_4^2^-])/([H_2PO_4^-])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/az25hcanq02r0fwg7tdnkm4gjhwsixtmbh.png)
![-0.34 = log ([HPO_4^2^-])/([H_2PO_4^-])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/bg8tcfy4xi8e0n8vwc7mcvb8qa1k5gry2l.png)
Removing log
![10^-^0^.^3^4 = ([HPO_4^2^-])/([H_2PO_4^-])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/vqhz41o2aktjgy75is57xuina2ycn2246d.png)
![([HPO_4^2^-])/([ H_2PO_4^-]) = 0.457](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/3jvz2ee11qnc9b7xe0kqvf7r2cz1zm0l24.png) ---------------- equation (1)
---------------- equation (1)
Step 3 : To find molarity of H₂PO₄⁻ and HPO₄²⁻
Total concentration of buffer = [H₂PO₄⁻] + [HPO₄²⁻] = 0.1 M
Hence, [H₂PO₄⁻ ] + [ HPO₄²⁻ ] = 0.1 M
Assume [H₂PO₄⁻ ] = x
So , [x ] + [ HPO₄²⁻ ] = 0.1 M
[ HPO₄²⁻ ] = 0.1 - x
Step 4 : Plugging value of [H₂PO₄⁻ ] and [ HPO₄²⁻ ]
[H₂PO₄⁻ ] = x
[ HPO₄²⁻ ] = 0.1 - x
Equation (1) = >
![([HPO_4^2^-])/([ H_2PO_4^-]) = 0.457](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/3jvz2ee11qnc9b7xe0kqvf7r2cz1zm0l24.png)
Plug value of [H₂PO₄⁻ ] and [ HPO₄²⁻ ] ( from step 3 ) into equation (1) as :
![([0.1 - x ])/([ x]) = 0.457](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/4rk0g0spp5vtsm13kuyecpt3h0nhr2zwx2.png)
Cross multiplying
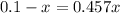
Adding x on both side
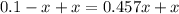
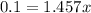
Dividing both side by 1.457
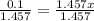
x = 0.0686 M
Hence , [H₂PO₄⁻ ] = x = 0.0686 M
[ HPO₄²⁻ ] = 0.1 - x
[ HPO₄²⁻ ] = 0.1 - 0.0686
[ HPO₄²⁻ ] = 0.0314 M
Step 5 : To find moles of H₂PO₄⁻ ( NaH₂PO₄) and HPO₄²⁻ (Na₂HPO₄ ) .
Molarity is defined as mole of solute per 1 L volume of solution .
Molarity of NaH₂PO₄ = 0.0686 M or 0.0686 mole per 1 L
Molarity of Na₂HPO₄ = 0.0314 M or 0.0314 mole per 1 L
Since that volume of buffer solution is 1 L , so Molarity = mole
Hence Mole of NaH₂PO₄ = 0.0686 mol
Mole of Na₂HPO₄ = 0.0314 mol
Step 6 : To find mass of Na₂HPO₄ and NaH₂PO₄
Moles of Na₂HPO₄ and NaH₂PO₄ can be converted to their masses using molar mass as follows :
Molar mass of Na₂HPO₄ =
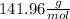
Molar mass of NaH₂PO₄ =
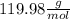
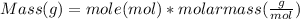
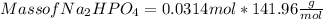
Mass of Na₂HPO₄ = 4.457 g
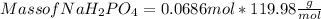
Mass of NaH₂PO₄ = 8.23 g