According to zeroth law of thermodynamics, when two objects are kept in contact, heat (energy) is transferred from one to the other until they reach the same temperature (are in thermal equilibrium). When the objects are at the same temperature there is no heat transfer.
So, at equilibrium,
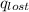 =
=
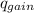 ,
,
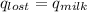 +
+
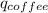
q=m×c×T, where q = heat energy, m = mass of a substance, c = specific heat (units J/kg∙K), T is temperature
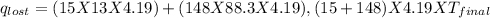 =(15X13X4.19)+(148X88.3X4.19)
=(15X13X4.19)+(148X88.3X4.19)
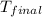 = 81.37 ° C
= 81.37 ° C