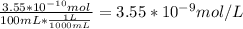a) 5.24μL He is present per L of air
Pressure, P = 1.000 atm
Volume, V =
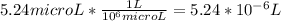
Temperature, T = 298.15 K
Using the ideal gas equation to find out moles of He,
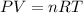
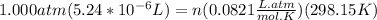
number of moles n =
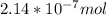
b) Concentration of Ar in % by volume in air = 0.93
That means 0.93 mL Ar is present in 100 mL of air
Moles of Ar =
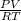
=
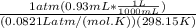 =
=
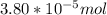
Molarity of Ar in air =
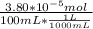
=
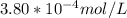
Similarly, mass % of Kr in air = 0.00011 % by volume
0.00011 mL Kr is present per 100 mL of air
Calculating moles of Kr:
n =
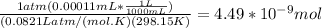
Molarity of Kr in air=
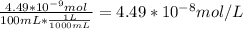
Mass % of Xe in air is 0.0000087 % by volume
0.0000087 mL Xe is present per 100 mL air
Calculating moles of Xe:
n =
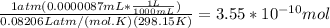
Molarity of Xe in air =