Answer : The molarity and molality of the solution is, 1.00 mole/L and 0.904 mole/Kg respectively.
Solution : Given,
Density of solution = 1.19 g/ml
Molar mass of sodium carbonate (solute) = 84 g/mole
7.06% aqueous solution of sodium bicarbonate means that 7.06 gram of sodium bicarbonate is present in 100 g of solution.
Mass of sodium bicarbonate (solute) = 7.06 g
Mass of solution = 100 g
Mass of solvent = Mass of solution - Mass of solute = 100 - 7.06 = 92.94 g
First we have to calculate the volume of solution.
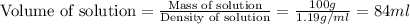
Now we have to calculate the molarity of solution.
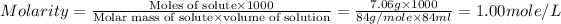
Now we have to calculate the molality of the solution.
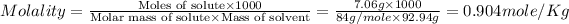
Therefore, the molarity and molality of the solution is, 1.00 mole/L and 0.904 mole/Kg respectively.