Decay of Ar-40 produces 1.33 mmol of K-40. Remaining number of moles of Ar-40 is 1.50 mmol. Initial mmol of Ar-40 present will be sum of number of moles of K-40 and remaining number of moles of Ar-40.
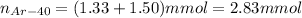
now, half life time of the reaction is
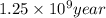
For first order reaction, rate constant and half-life time are related to each other as follows:
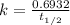
Putting the value of
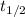 ,
,
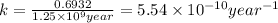
Rate equation for first order reaction is as follows:
![t=(2.303)/(k)log([A_(0)])/([A_(t)])}](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/physics/college/yh0p148ej0qr91vh74ds0ji7oheo7mixk5.png)
Here,
![[A_(0)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/physics/college/vnp7p4lqnfvofj9dohr7nisdobp6edklz1.png) is initial concentration and
is initial concentration and
![[A_(t)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/physics/college/igtrnnvfmc40l91yok2ptjevfkt41klbyn.png) is concentration at time t.
is concentration at time t.
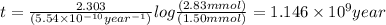
Therefore, time required to cool the rock is
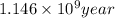 .
.