The mass of impure
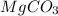 is 20.7167 g. The decomposition reaction is as follows:
is 20.7167 g. The decomposition reaction is as follows:
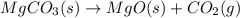
Here, 1 mole of
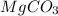 gives 1 mole of MgO.
gives 1 mole of MgO.
Molar mass of
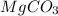 and MgO is 84.31 g/mol and 40.3044 g/mol respectively.
and MgO is 84.31 g/mol and 40.3044 g/mol respectively.
Converting number of moles in terms of mass,
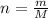
Here, M is molar mass.
Since,
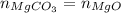
Thus,
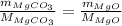
On putting the values,
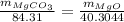
Rearranging,
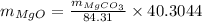
Or,
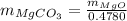 ...... (1)
...... (1)
Let the mass of impurity be
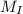 and mass of impure
and mass of impure
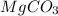 is 20.7167 g thus,
is 20.7167 g thus,
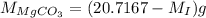 ...... (2)
...... (2)
Also, mass of impure MgO is 16.8817 g thus,
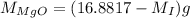 ...... (3)
...... (3)
On comparing equations (2) and (3),
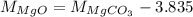
Putting the value of
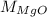 in equation (1),
in equation (1),
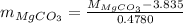
Or,
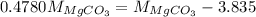
Or,
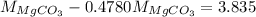
Or,
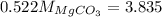
Or,
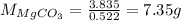
Thus, magnesium carbonate present in the original sample is 7.35 g.