The chemical reaction is as follows:
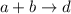
Mass of reactant a is 1 g and molar mass is 94 g/mol. Converting mass into number of moles as follows:
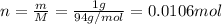
Now, 1 mole of reactant a gives 1 mole of product d thus, 0.0106 mol of reactant a gives 0.0106 mol of product d.
Molar mass of product d is 125 g/mol, converting number of moles into mass as follows:
m=n×M=0.0106 mol×125 g/mol=1.33 g
Similarly, molar mass of reactant b is 118 g/mol and mass is 2 g, converting mass into number of moles,
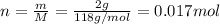
1 mol of reactant b gives 1 mol of product d thus, 0.017 mol will give 0.017 mol of product d.
Converting number of moles into mass as follows:
m=n×M=0.017 mol×125 g/mol=2.12 g
Here, reactant that produces lesser product is limiting reactant and the amount of product it forms is theoretical yield.
Therefore, theoretical yield is 1.33 g.