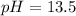
Step-by-step explanation:
Sodium hydroxide completely ionizes in water to produce sodium ions and hydroxide ions. Hydroxide ions are in excess and neutralize all acetic acid added by the following ionic equation:
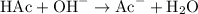
The mixture would contain
if
 undergoes no hydrolysis; the solution is of volume
undergoes no hydrolysis; the solution is of volume
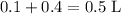 after the mixing. The two species would thus be of concentration
after the mixing. The two species would thus be of concentration
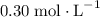 and
and
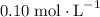 , respectively.
, respectively.
Construct a RICE table for the hydrolysis of
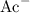 under a basic aqueous environment (with a negligible hydronium concentration.)
under a basic aqueous environment (with a negligible hydronium concentration.)
![\begin{array}{cccccccc} \text{R} & \text{Ac}^(-)(aq) &+ & \text{H}_2\text{O}(aq) & \leftrightharpoons & \text{HAc}(aq) & + & \text{OH}^(-) (aq)\\ \text{I} & 0.10 \; \text{M} & & & & & &0.30 \; \text{M}\\ \text{C} & -x \; \text{M}& & & & +x \; \text{M}& & +x \; \text{M} \\ \text{E} & (0.10 - x) \; \text{M} & & & & x \; \text{M} & & (0.30 +x) \; \text{M} \end{array}]()
The question supplied the acid dissociation constant
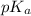 for acetic acid
for acetic acid
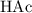 ; however, calculating the hydrolysis equilibrium taking place in this basic mixture requires the base dissociation constant
; however, calculating the hydrolysis equilibrium taking place in this basic mixture requires the base dissociation constant
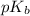 for its conjugate base,
for its conjugate base,
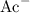 . The following relationship relates the two quantities:
. The following relationship relates the two quantities:
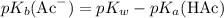
... where the water self-ionization constant
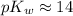 under standard conditions. Thus
under standard conditions. Thus
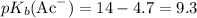 . By the definition of
. By the definition of
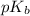 :
:
![[\text{HAc} (aq)] \cdot [\text{OH}^(-) (aq)] / [\text{Ac}^(-) (aq) ] = K_b = 10^{-pK_(b)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/t582m55jbc7v5xqy8ylybc1x007i8hzqbo.png)
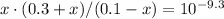
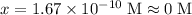
![[\text{OH}^(-)] = 0.30 +x \approx 0.30 \; \text{M}](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/rccnfqef25rjn2hm7awdfs6s9tnqizzv0o.png)
![pH = pK_(w) - pOH = 14 + \text{log}_(10)[\text{OH}^(-)] = 14 + \text{log}_(10){0.30} = 13.5](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/4edn81qfzzjeuaejy9cuxxna8kiyqklx1p.png)