The original milk sample contained 54000 cells per milliliter of the milk.
Plate count assay is used to identify the number of viable cells in a sample given. It is done by the serial dilution technique which is the step wise dilution of a substance in a sample. Serial dilution is followed by plating technique which helps in finding individual dilutions, finding serial dilutions and the number of organisms present in the original sample.
In the question, one-milliliter sample of the milk is diluted in a 1:10 dilution series and one milliliter of the third dilution tube is plated in a pour plate. After incubation, the plate shows 54 colonies. Third dilution is represented by
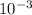 . The formula used for the calculation of the number of organisms present in the original sample of milk is number of colonies growing on the plate x (1 x volume used to plate bacteria) x (1/dilution). By substituting the values given,
. The formula used for the calculation of the number of organisms present in the original sample of milk is number of colonies growing on the plate x (1 x volume used to plate bacteria) x (1/dilution). By substituting the values given,
No. of organisms in the original milk sample
= 54 x (1 x 1ml) x (1/
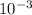 )
)
= 54 x 1 /
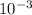
= 54000.