Volume of Oxygen O2 would be 33 L.
Solution : Given information - Mole (n) = 6.9 mol
Pressure (P) = 4.0 atm
Temperature (T) = 233 K
Universal gas constant (R) = 0.0821 L.atm/mol.K
Volume(V) is unknown , which we need to find.
Volume can be calculated by using the Ideal gas equation which is :
PV = nRT (Ideal gas equation)
On rearranging the above formula we will get :
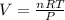
Where , P = pressure , V = volume , n = mole , R = universal gas constant , T = temperature.
We will plugin the values of P , n , R and T in the ideal gas equation and then calculate Volume (V)
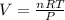
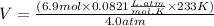
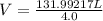
V = 32.998 L or 33 L