Answer:
Option (b)
Step-by-step explanation:
Let the initial speed of the car is u and the final speed is zero. Let mass of the car is m.
Case I
Acceleartion of the car, a = - F/m
Use III equation of motion,
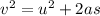
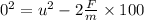
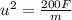 ...... (1)
...... (1)
Case II
Acceleration of the car, a = - 0.8 F/m
Use III equation of motion,
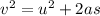
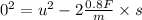
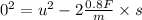
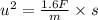 ..... (2)
..... (2)
Dividing equation (2) by equation (1), we get
s = 125 m