Answer:- Mole fraction of methane in the original gas mixture is 0.854.
Solution:- From given volume, pressure and temperature, we could calculate the total moles of the gaseous mixture of methane and propane using ideal gas law as:
PV = nRT
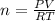
V = 2.50 L
P = 1.45 atm
T = 20 + 273 = 293 K
Let's plug in the values in the equation:
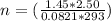
n = 0.151
Let's say the solution has X moles of methane. Then moles of propane would be = (0.151 - X)
The combustion equations of methane and propane are:
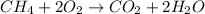
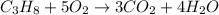
From methane balanced equation, there is 1:1 mol ratio between methane and carbon dioxide. So, X moles of methane would produce X moles of carbon dioxide.
From balanced equation of propane, there is 1:3 mol ratio between propane and carbon dioxide. So, (0.151 - X) moles of propane would give 3(0.151 - X) moles of carbon dioxide.
So, total moles of carbon dioxide that we would get from methane and propane combustion are:
X + 3(0.151 - X)
From given data, 8.60 g of carbon dioxide are formed by the combustion of gas mixture.
moles of Carbon dioxide =
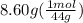
moles of carbon dioxide = 0.195 mol
Hence, 0.195 = X + 3(0.151 - X)
Let's solve this for X as:
0.195 = X + 0.453 - 3X
0.195 = 0.453 - 2X
2X = 0.453 - 0.195
2X = 0.258
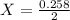
X = 0.129
So, there are 0.129 moles of methane in the mixture.
moles of propane = 0.151 - 0.129 = 0.022
mole fraction of methane =
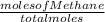
mole fraction of methane =
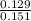
mole fraction of methane = 0.854
Hence, the mole fraction of methane gas in the original gas mixture is 0.854.