Answer:- 8.89 g of carbon dioxide can be produced.
Solution:- The balanced equation for the combustion of octane in presence of oxygen to give carbon dioxide and water is:
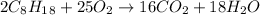
From given info, we have 6.9 g octane and 10.1 g oxygen and asked to calculate the maximum mass of carbon dioxide formed.
It is a stoichiometry problem. Let's first figure out the limiting reactant. For this we could either calculate grams of octane required to react completely with given grams of oxygen or vice versa.
From balanced equation, there is 25:2 mol ratio between oxygen and octane.
Let's say we calculate grams of oxygen for given grams of octane as:
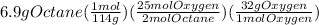
= 24.1 g oxygen
From calculations, 24.1 g of oxygen are required to react completely with 6.9 g of octane but in actual only 10.1 g of oxygen are available. So, oxygen is limiting reactant and so the product yield depends on it and calculated as:
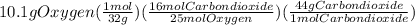
= 8.89 g carbon dioxide
So, from given masses of octane and oxygen, maximum 8.89 g of carbon dioxide can be produced.