So, with rational equations, we have three different cases. If the numerator has degree m and the denominator degree n, if m>n, the rational equation has an oblique(slant) asymptote. If m=n, the asymptote is the quotient of the leading coefficient of the numerator divided by the leading coefficient of the denominator. If m<n, the rational equation has an asymptote at 0. Since m>n in this problem, we must perform polynomial division.
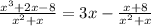
Since the remainder tends to 0 as it approaches infinity, we have a slant asymptote at y=3x.