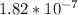The equilibrium equation showing the dissociation of weak acid is:
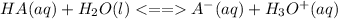
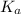 is the equilibrium constant for this equation, which is referred to as the acid dissociation constant.
is the equilibrium constant for this equation, which is referred to as the acid dissociation constant.
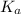 value will determine the acidic strength of the acids. Greater the value, more will be the acidity.
value will determine the acidic strength of the acids. Greater the value, more will be the acidity.
Calculating the
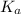 value from given equilibrium concentrations:
value from given equilibrium concentrations:
![K_(a) = ([H_(3)O^(+)][A^(-)])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/jgnkdvpkaq2s64ljcccnxsy8wt1eucycwn.png)
=
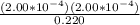
=