Answer:- Equilibrium partial pressure of NO is 0.50 atm and equilibrium partial pressure of
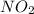 = 0.02 atm.
= 0.02 atm.
Solution:- Let's say the initial pressure of
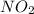 is p. We would make the ICE table for the given equation and consider the change in pressure as X.
is p. We would make the ICE table for the given equation and consider the change in pressure as X.
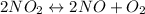
I P 0 0
C -2X +2X +X
E (P-2X) 2X X
From given information, equilibrium partial pressure of oxygen is 0.25 atm and from ICE table it is X.
So, X = 0.25
equilibrium partial pressure of NO = 2(0.25 atm) = 0.50 atm
and equilibrium partial pressure of nitrogen dioxide = P-0.50
For the equation we have, the Kc expression would be written as:
![Kp=(([NO]^2[O_2])/([NO_2]^2))](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/73glp5u8n3ltabpxi23xmd2fkplvpc2afp.png)
Let's plug in the values in this expression:
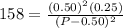
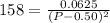
This could also be written as:
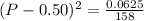
On taking square root to both sides:
(P-0.50) = 0.0199
add 0.50 to both sides:
P = 0.0199 + 0.50
P = 0.5199 and it's rounded off to 0.52
Now, we could calculate the equilibrium partial pressure of nitrogen dioxide as:
equilibrium partial pressure of nitrogen dioxide = P-0.50
equilibrium partial pressure of nitrogen dioxide = 0.52-0.50 = 0.02 atm
So, equilibrium partial pressure of
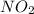 = 0.02 atm
= 0.02 atm
equilibrium partial pressure of NO = 0.50 atm and